[Design Pattern] Abstract Factory Pattern
Mục lục
- Phần 1: Factory Method
- Phần 2: Abstract Factory
- Phần 3: Builder
- Phần 4: Prototype
- Phần 5: Singleton
- Phần 6: Adapter
- Phần 7: Bridge
Phần 2: Abstract Factory
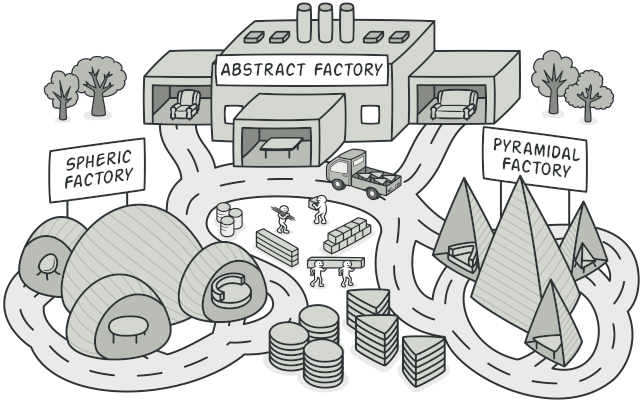
Abstract Factory cho phép ta có thể tạo một tập các objects liên quan đến nhau mà không cần phải thông qua các classes cụ thể nào.
Vấn đề
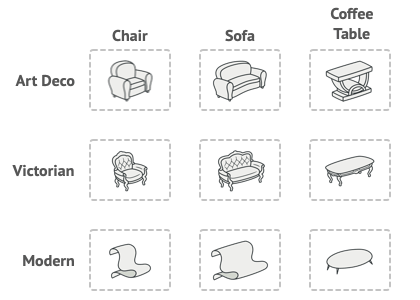
Giả sử bạn đang dev một shop simulator về đồ nội thất, code của bạn gồm các classes:
- Các đồ dùng gia đình:
Chair+Sofa+Coffee Table - Các kiểu dáng:
Modern,Victorian,ArtDeco
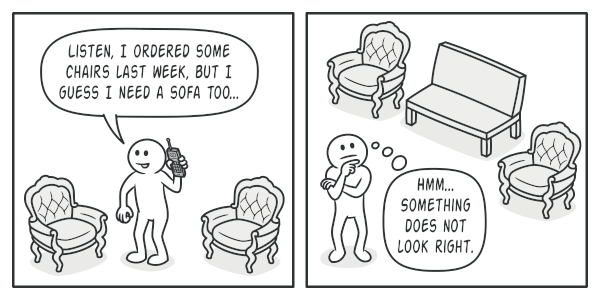
Bạn muốn bán cho khách hàng đúng loại đồ nội thất mà họ muốn, đồng thời đáp ứng kịp thời cho sự thay đổi catalog của nhà cung cấp mà không cần phải thay đổi core code.
Giải pháp
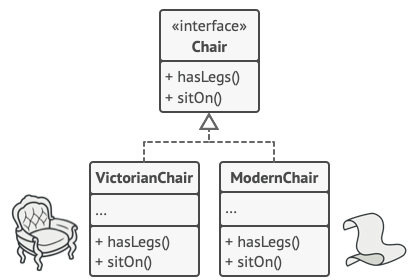
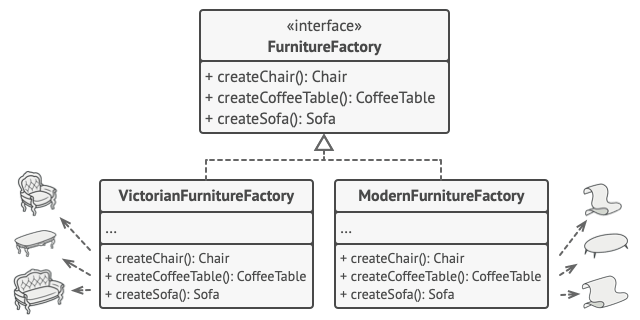
Abstract Factory sẽ xử lí vấn đề bằng cách tạo ra các interfaces cho các đồ dùng (VD: Chair, Sofa, Coffee Table). Sau đó các kiểu dáng sẽ là các class implements các interfaces trên.
Tiếp theo đó là tạo Abstract Factory - bản chất là một interface với các methods tạo ra các đồ nội thất Chair, Sofa, … tương ứng là createChair, createSofa. Các methods này sẽ trả về các abstract product type mà ta đã định nghĩa thông qua các interface Chair, Sofa, …
Với các kiểu dáng, ta sẽ tạo ra các Factory class implement Abstract Factory ở trên, với các methods sẽ trả về (ModernChair, ModernSofa tương ứng với createChair() và createSofa()).
Do phía client không quan tâm đến class cụ thể của factory, nên ta có thể truyền xuống cho client code (kiểu dáng cũng như factory type).
Phía client sẽ xử lí các loại Chair như VictorianChair hoặc ModernChair như nhau vì đều là Chair (abstract interface). Với cách tiếp cận này thì client chỉ có thể biết về method sitOn() của Chair mà thôi. Hơn nữa Sofa và CoffeeTable được trả về sẽ luôn đồng loại với Chair.
Còn một vấn đề nữa đó là khi client chỉ sử dụng interface của factory thôi thì sao ? Khi đó factory object sẽ được khởi tạo từ ban đầu, bản thân factory type sẽ được lấy từ các biến môi trường hoặc các biến config.
Cấu trúc
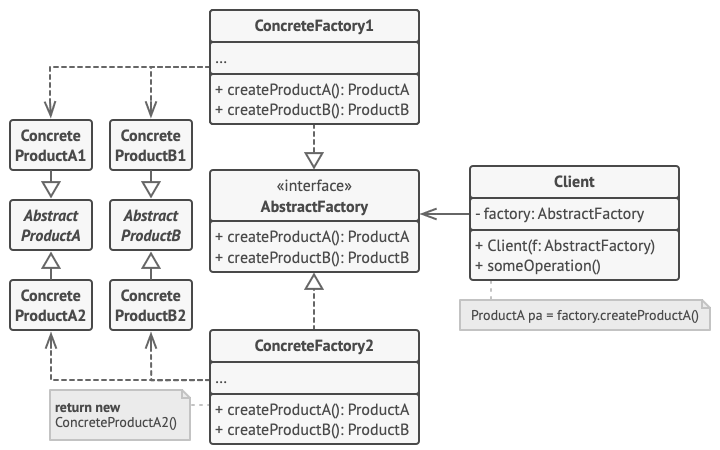
- Abstract Product: các interfaces định nghĩa các product liên quan.
- Concrete Product: triển khai các
abstract productsnhóm theo các kiểu dáng. Mỗi abstract product phải được triển khai toàn bộ các kiểu dángModern,ArtDeco, … - Abstract Factory: interface định nghĩa các methods tạo các
Abstract Product. - Concrete Factory: triển khai
Abstract Factory, với các methods tạo ra các products thuộc cùng một kiểu dáng. - Dù
Concrete Factorytạo ra cácConcrete Productxong chữ kí các hàm creation của nó sẽ phải trả vềAbstract Product
Source code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
interface AbstractProductA {
usefulFunctionA(): string;
}
interface AbstractProductB {
usefulFunctionB(): string;
anotherUsefulFunctionB(collaborator: AbstractProductA): string;
}
interface AbstractFactory {
createProductA(): AbstractProductA;
createProductB(): AbstractProductB;
}
class ConcreteProductA1 implements AbstractProductA {
usefulFunctionA(): string {
return "The result of the product A1.";
}
}
class ConcreteProductA2 implements AbstractProductA {
usefulFunctionA(): string {
return "The result of the product A2.";
}
}
class ConcreteProductB1 implements AbstractProductB {
usefulFunctionB(): string {
return "The result of the product B1.";
}
anotherUsefulFunctionB(collaborator: AbstractProductA): string {
const result = collaborator.usefulFunctionA();
return `The result of the B1 collaborating with the (${result})`;
}
}
class ConcreteProductB2 implements AbstractProductB {
usefulFunctionB(): string {
return "The result of the product B2.";
}
anotherUsefulFunctionB(collaborator: AbstractProductA): string {
const result = collaborator.usefulFunctionA();
return `The result of the B2 collaborating with the (${result})`;
}
}
class ConcreteFactory1 implements AbstractFactory {
createProductA(): AbstractProductA {
return new ConcreteProductA1();
}
createProductB(): AbstractProductB {
return new ConcreteProductB1();
}
}
class ConcreteFactory2 implements AbstractFactory {
createProductA(): AbstractProductA {
return new ConcreteProductA2();
}
createProductB(): AbstractProductB {
return new ConcreteProductB2();
}
}
function clientCode(factory: AbstractFactory) {
const productA = factory.createProductA();
const productB = factory.createProductB();
console.log(productB.usefulFunctionB());
console.log(productB.anotherUsefulFunctionB(productA));
}
console.log("Client: Testing client code with the first factory type...");
clientCode(new ConcreteFactory1());
console.log("");
console.log("Client: Testing client code with the second factory type...");
clientCode(new ConcreteFactory2());